Hypothyroidism is a condition that affects millions of people around the world. It causes many physical and psychological symptoms, as well as disrupting normal bodily functions.
This article provides an overview of hypothyroidism, describing its symptoms, possible causes, and available treatments. We’ll also discuss how to manage the condition daily so you can live your life with greater peace of mind.
Hypothyroidism is not something to be taken lightly; it can have serious consequences if it goes untreated or is managed incorrectly. With knowledge comes power; understanding this medical condition will enable you to take control and ensure that your health remains in good shape.
Introduction to Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition that affects the body’s ability to produce hormones needed for proper metabolic activity. It occurs when the thyroid gland does not make enough of these hormones, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, it can be managed effectively. In this article, we will discuss the various causes of hypothyroidism, its associated symptoms, and the treatments available.
We will also look at how lifestyle changes may help reduce your risk of developing hypothyroidism or improve your quality of life if you already have it. By understanding more about what hypothyroidism is and how it works in our bodies we can better equip ourselves to take control of our health and well-being!
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism

Common symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, dry skin, and hair, joint pain and stiffness, muscle weakness, weight gain or difficulty losing weight despite diet and exercise plans, a slowed heart rate, depression or other mental health issues, constipation, or digestive problems. Other signs can include an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter), a hoarse voice due to swollen vocal cords in the larynx (voice box) as well and increased sensitivity to cold temperatures.
In some cases, an individual may not experience any physical symptoms at all but still be diagnosed with hypothyroidism.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune condition called Hashimoto’s disease, in which the body attacks its thyroid gland. Other possible causes include radiation therapy or surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid, certain medications, iodine deficiency, and congenital (inborn) conditions such as goiters.
Sometimes a malfunctioning pituitary gland can lead to hypothyroidism by not signaling the production of enough TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone). Thyroiditis—inflammation of the thyroid—can also be a cause.
In rare cases, too much iodine can cause hypothyroidism; however, this is uncommon since many people don’t get enough iodine in their diets.
Treatments for Hypothyroidism

When it comes to treating hypothyroidism, the primary goal is to restore hormone levels to normal. The most common treatment for this condition is daily doses of an oral replacement thyroid hormone called levothyroxine.
This medication helps replace the hormones that your body can no longer make on its own and can be taken just once a day in pill form with food or water. Other treatments may include dietary changes such as avoiding foods high in iodine, taking supplements with vitamins and minerals like zinc, vitamin B12, and selenium, and lifestyle modifications like reducing stress levels and getting more sleep.
In some cases of severe hypothyroidism, surgery may be an option to remove part or all of the thyroid gland if other treatments are not effective. It’s important to speak with your doctor about any concerns you have regarding which treatment plan is best suited for you so they can help guide you towards making an informed decision about your health care needs.
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones to meet the body’s needs. It can cause symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, depression, constipation, and dry skin.
The causes of hypothyroidism can be genetic or due to an autoimmune disorder like Hashimoto’s disease. Treatment for hypothyroidism may include taking medications that contain synthetic versions of thyroxine hormone or natural desiccated thyroid supplements.
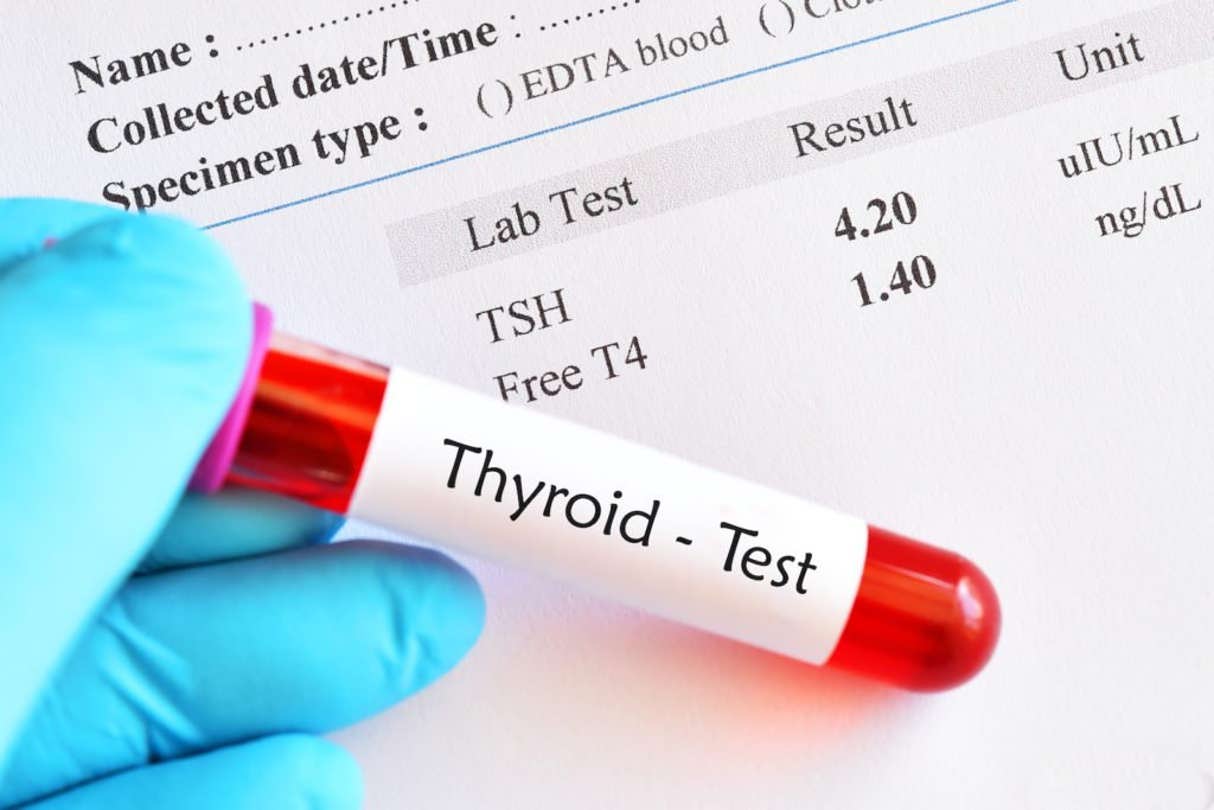
In some cases, dietary changes may also help manage symptoms associated with this condition. To diagnose hypothyroidism a doctor may order blood tests that measure levels of TSH and other hormones produced by the thyroid gland; it is even possible to have a thyroid test at home if you want to check your thyroid level before consulting with a physician. With proper diagnosis and treatment from your doctor, many people living with hypothyroidism can control their symptoms and lead healthy lives.